application of organic adaptation laws as theoretical basis of the rehabilitational protocol
The organic adaptation uses that chain of physiological responses, defined by Selye as General Adaptation Syndrome, consequent to a stress situation such as trauma, diseases, strong emotions, work in motion , ecc...
The reactions chain is divided into answers:
- Non specific of short-term and of low - intensity followed by very pronounced phenomena with the peculiarity of being always the same , independently from the stressor agent that affects the body: trauma, disease , emotion, work in motion, ecc.;
- Specific tend to increase one or more biological functions with summation effect after constant repeability of stress or understood as a repetition of specific working in motion.
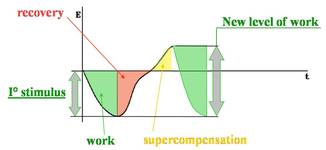
The response phenomena "very pronounced" and " summation effect" , are the basis of adaptation of an organic function that is of the modification of specific structure oriented to bear increasingly heavy situations.
For this to happen mechanical /in motion stimulus must be programmed in a sequential and growing way: in fact if the first exposition was not too severe and the duration of the resting phase was sufficient, the next exposition finds the body already prepared and with a top degree of adaptation from the start , because the body always repays the work done with an higher level than consumed (very pronounced reponse ); this increase in energy availability is defined "supercompensation ".
This leads to a subsequent increase in resistance to specific stimulus compared to the initial, provided the time elapsed between the two expositions is not excessive and the body retaining the memory.
In this case, a new exposition well-dosed even if more intense than the previous, will further increase the adaptation and resistance capacity;
In this way we will have for shelves, an increase in capacity preparing the system to increasingly intense loads.
The reactions chain is divided into answers:
- Non specific of short-term and of low - intensity followed by very pronounced phenomena with the peculiarity of being always the same , independently from the stressor agent that affects the body: trauma, disease , emotion, work in motion, ecc.;
- Specific tend to increase one or more biological functions with summation effect after constant repeability of stress or understood as a repetition of specific working in motion.
The response phenomena "very pronounced" and " summation effect" , are the basis of adaptation of an organic function that is of the modification of specific structure oriented to bear increasingly heavy situations.
For this to happen mechanical /in motion stimulus must be programmed in a sequential and growing way: in fact if the first exposition was not too severe and the duration of the resting phase was sufficient, the next exposition finds the body already prepared and with a top degree of adaptation from the start , because the body always repays the work done with an higher level than consumed (very pronounced reponse ); this increase in energy availability is defined "supercompensation ".
This leads to a subsequent increase in resistance to specific stimulus compared to the initial, provided the time elapsed between the two expositions is not excessive and the body retaining the memory.
In this case, a new exposition well-dosed even if more intense than the previous, will further increase the adaptation and resistance capacity;
In this way we will have for shelves, an increase in capacity preparing the system to increasingly intense loads.
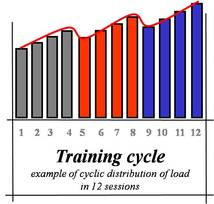
A proper organization of rehabilitation work, then, should provide a rational and progressive distribution of work loads in between the various sessions that should be gradually and progressively increased, but alternating with specific relief phases (during which load must decrease) and of rest.
In this periods that organic adaptation happens, that is the settlement of those mechanisms that repays the work done, increasing and cementing the functional reserves and preparing the biological system to an heavy situation.
In this periods that organic adaptation happens, that is the settlement of those mechanisms that repays the work done, increasing and cementing the functional reserves and preparing the biological system to an heavy situation.
Specifically , the programming of activity in motion oriented to the functional recovery of the knee cartilage must provide a precise consequentiality of "pressure" stimulus (alternation compression/recovery) generated by the deambulatory action during which the visco - elastic process of "damping " of cartilage is reactivated and programmable by " deambulation speed distance to go, recovery time ".